|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Create Custom Data Set |
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Create Custom Data Set |
|
You can follow these steps to create your custom data set on V6.0 till the latest version.
1) Click the quick start shortcut of Yonghong Z-Suite.
2) Open the browser and enter http://hostname:8080/bi/Viewer in the address bar to log in to the client. The hostname here refers to the IP address of your PC. For local visit, you can use localhost. 8080 is the default port number. If the default port number is changed during installation, type in the correct port number.
3) Enter username and password and then log in the homepage.
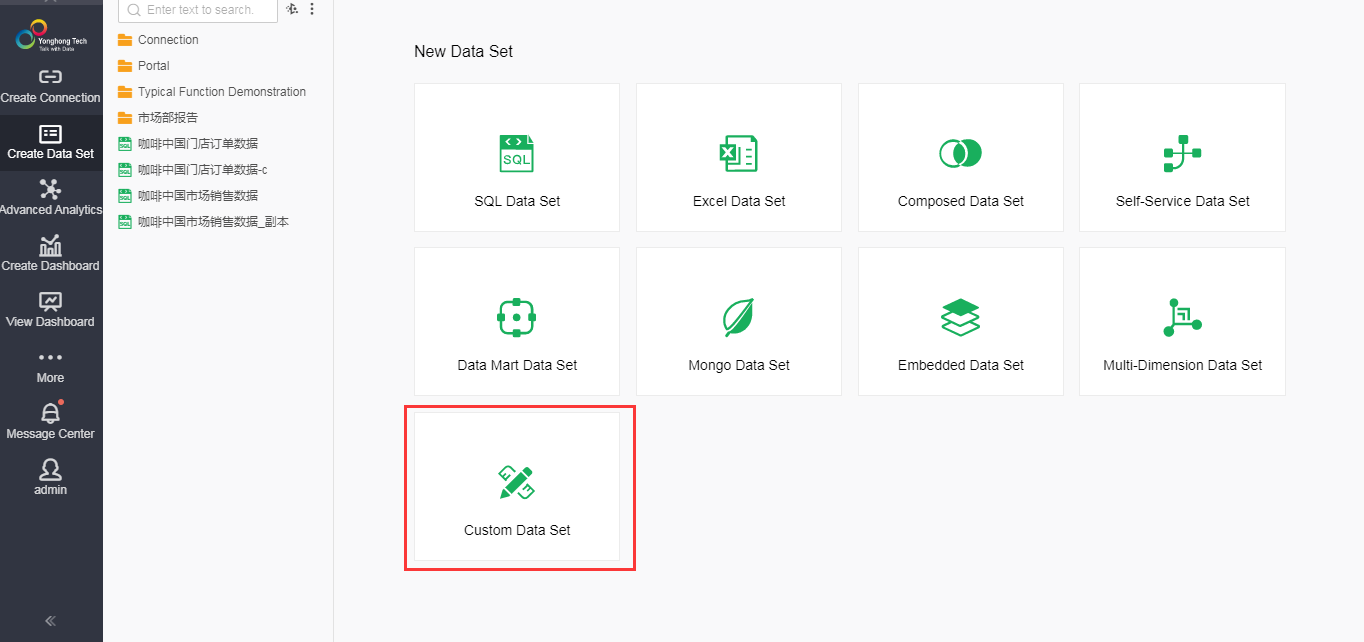
4) Click "Create Data Set" to enter the page for creating a data set.
Click on the "Custom Data Set" option on the page to open the Custom Data Set interface.
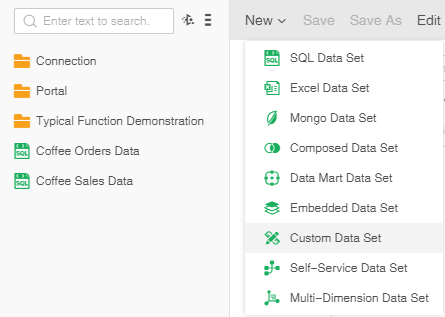
On the data set page, click "New" on the menu bar and select "Custom Data Set" to open Custom Data Set page.
Custom Data Set interface:
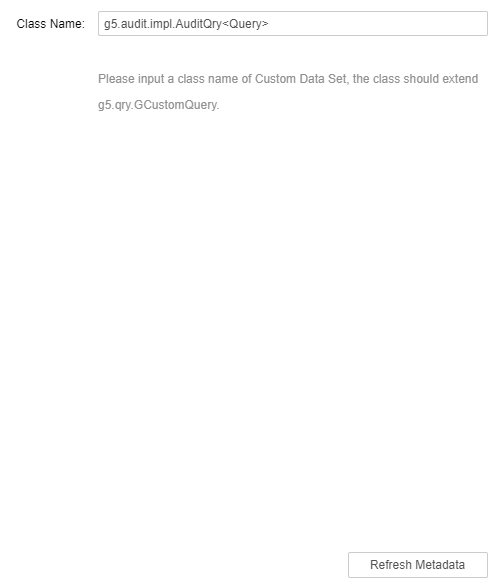
5) Fill in the complete class path of the custom query you developed, such as com.yonghongtech.query.CustomQuery, and then refresh the metadata and save it.
❖Related classes and interfaces
•g5.qry.GcustomQuery
Developing custom queries first needs to inherit this class. Then three methods need to be implemented.
1. public DataGrid exec(QCol[] qCols, QContext qContext)
This method implements its own logic, and then stores the data in QGrid and returns.
2. public QCol[] metaCols(QContext qContext)
Create a QCol array to store all fields.
3. public Query createRuntime(QContext qContext)
just return this
4. public boolean isDynamic()
When the number of fields is not fixed, you need to override this method and return true.
5. Construction method
When you need to pass some parameters through the construction method, you can write another construction method. In this case, you need to fill in the <parameter> after the class name in the "class name" of the custom query. Multiple parameters are separated by commas, and no spaces are allowed, for example :
com.yonghongtech.query.MongoZhiwenOffers <true, false>
•g5.DataGrid
It is used to store data and is an interface. QGrid is generally used when developing custom queries.
public void add(int c, Object obj)
Use the add method to store the data in QGrid, and finally return.
•g5.meta.QCol
It represents the queried fields.QCol is an interface, and g5.meta.BCol can be used in custom queries.
public BCol(String name, String view, byte dtype, boolean dim)
The meaning of the four parameters of its construction method are:
name: field name
view: Alias
dtype: type
dim: whether it is a dimension
The correct construction method can be selected according to actual needs to construct BCol.
❖Sample code
public class CQuery extends GCustomQuery {
@Override
public DataGrid exec(QCol[] qCols, QContext qContext) throws Exception {
QGrid qgrid = create(qContext);
MongoClient client = MongoUtil.getClient("zhiwen");
FindIterable<Document> documents = MongoUtil.getAllDocument(client, "zhiwen", "offers");
for(Document document : documents) {
Object company = document.get("company");
Object date = document.get("date");
Object industry = document.get("industry");
Object ownerId = document.get("ownerId");
Object type = document.get("type");
Object recommendation = document.get("recommendation");
qgrid.add(0, String.valueOf(company));
qgrid.add(1, date);
qgrid.add(2, String.valueOf(industry));
qgrid.add(3, String.valueOf(ownerId));
qgrid.add(4, String.valueOf(type));
qgrid.add(5, String.valueOf(recommendation));
}
client.close();
qgrid.complete();
return qgrid;
}
@Override
public QCol[] metaCols(QContext qContext) throws Exception {
return new QCol[]{new BCol("company", DType.STRING, true),
new BCol("date", DType.DATE_TIME, true),
new BCol("industry", DType.STRING, true),
new BCol("ownerId", DType.STRING, true),
new BCol("type", DType.STRING, true),
new BCol("recommendation", DType.STRING, true)};
}
protected QGrid create(QContext context) {
QCol[] cols = new QCol[0];
try {
cols = metaCols(context);
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String[] harr = new String[cols.length];
byte[] sarr = new byte[cols.length];
for(int i = 0; i < cols.length; i++) {
harr[i] = cols[i].getView();
sarr[i] = DynamicObjectSeg.getPreferredSeg(cols[i].getDType(), false);
}
return (QGrid) QGrid.create(harr, sarr, cols);
}
@Override
public Query createRuntime(QContext qContext) {
return this;
}
}
The create method does not need to be changed, only the other three methods need to be implemented.
❖Deployment and Test
•Deployment
Compile the program into a class file. Then put it in different directories according to different versions for testing
Version |
Directory |
6.0/6.1 |
tomcat/bi/WEB-INF/classes |
7.0 and after |
tomcat/webapps/bi/WEB-INF/classes |
•Test
When creating a custom data set, fill in the correct class name, refresh the metadata, and preview the data. If there is no error, it means the data set is created successfully.
❖Complete Program
